Are you concerned about potential lawsuits due to web accessibility and inaccessible web design? By 2025, accessible websites will be crucial for businesses to avoid legal issues and serve all users effectively. This guide covers key strategies, including implementing WCAG 3.0, using AI for accessibility, and optimising for mobile and assistive technologies.
You’ll learn how to create inclusive web experiences that comply with accessibility guidelines and meet the needs of users with disabilities.
Key Takeaways
- Prioritise web accessibility to ensure your digital content reaches all users, including those with disabilities
- Implement WCAG 3.0 guidelines to improve colour contrast, keyboard navigation, and overall accessibility compliance
- Use AI and machine learning to enhance accessibility testing, personalise experiences, and improve navigation
- Design for mobile accessibility with responsive layouts, optimised touch targets, and simplified navigation
- Conduct regular accessibility audits and address issues promptly to maintain compliance and improve user experience

As you prepare for 2025, prioritise web accessibility to ensure your digital content reaches all users, including those with visual impairments. Implement screen reader compatibility and proper use of alt attributes to make your website more inclusive and compliant with accessibility standards.
Embrace regulatory compliance as a key driver for accessible web design. Stay informed about evolving accessibility laws and guidelines to avoid legal issues and demonstrate your commitment to digital inclusivity.
Remember that accessible web design benefits everyone, not just users with disabilities. These strategies will create a more user-friendly website that improves the overall user experience and boosts your search engine rankings.
Adopt Universal Design Principles for Accessibility
Universal design principles are crucial for creating accessible websites that cater to diverse user needs. By understanding the seven principles and incorporating inclusive design from the start, you can address various abilities and ensure flexibility in UI design. This approach, aligned with World Wide Web Consortium guidelines and the Americans with Disabilities Act, minimises physical effort and provides perceptible information, making your site compatible with assistive technology like AccessiBe.
Understand the Seven Principles of Universal Design
The seven principles of universal design provide a framework for creating accessible websites that cater to all users, including those with disabilities. These principles encompass equitable use, flexibility, simple and intuitive operation, perceptible information, tolerance for error, low physical effort, and size and space for approach and use. By applying these principles, you can ensure your website complies with Equal Employment Opportunity Commission guidelines and provides reasonable accommodation for all users, enhancing safety and usability. The United States Department of Justice recognises these principles as essential for creating inclusive digital spaces that meet the needs of diverse populations.
Incorporate Inclusive Design From Project Inception
To create genuinely accessible websites, you must incorporate inclusive design principles from the start of your project. By considering the needs of all users, including those with disabilities, you’ll build a more robust and user-friendly site. This approach aligns with UK law and helps ensure equal internet access for your entire community. Developing a comprehensive knowledge base on accessibility standards will guide your design decisions and foster a more inclusive digital environment.
Address Diverse Needs and Abilities of Users
As you develop your website, consider users’ diverse needs and abilities to enhance internet accessibility. The Good Things Foundation emphasises digital literacy as a key factor in productivity and innovation. By addressing various user requirements, you’ll create a more inclusive online experience that accommodates different levels of ability, fostering greater engagement and usability across your audience:
| User Group | Accessibility Need | Design Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Visually impaired | Screen reader compatibility | Proper HTML structure and alt text |
| Hearing impaired | Visual alternatives for audio | Captions and transcripts |
| Motor impaired | Keyboard navigation | Focus indicators and skip links |
| Cognitive impaired | Clear, simple content | Consistent layout and plain language |
Ensure Flexibility and Simplicity in UI Design
To enhance digital literacy and accessibility, ensure your UI design is flexible and simple. Use a screen magnifier-friendly layout with clear, contrasting elements that work well with assistive software. Design your interface to be navigable without a computer mouse, accommodating various input methods. This approach not only aids users with disabilities but also improves usability for everyone, regardless of their computer skills or preferred interaction methods:
- Use scalable fonts and responsive layouts
- Implement keyboard shortcuts for all functions
- Provide clear, descriptive labels for all interactive elements
- Ensure sufficient colour contrast for better readability
- Create a consistent navigation structure across all pages

Provide Perceptible Information to Users
To enhance user experience design, provide perceptible information through inclusive design practices. Use clear, high-contrast text and images that are easily readable for all users, including those with visual impairments. Consider incorporating braille displays or audio descriptions for complex visuals. Ensure your design accommodates various sensory needs, making information accessible through multiple channels:
| Sensory Channel | Design Consideration | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Visual | High contrast, scalable text | Dark text on a light background |
| Auditory | Captions and transcripts | Video subtitles |
| Tactile | Braille support | Braille display compatibility |
| Cognitive | Clear, simple language | Concise instructions |
Minimise Physical Effort in User Interactions
To enhance web accessibility, design your user interface to minimise physical effort. Create web content that’s easy to navigate with simple gestures or keyboard commands. Your web page layout should support efficient interaction, reducing the need for repetitive actions. This approach aligns with the Web Accessibility Initiative’s guidelines, making your site more inclusive for users with motor impairments:
| Interaction Type | Accessibility Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse | Large clickable areas | Easier targeting for users with limited dexterity |
| Keyboard | Logical tab order | Efficient navigation without a mouse |
| Touch | Swipe gestures | Simplified interaction on mobile devices |
| Voice | Speech recognition | Hands-free control for motor-impaired users |
Implement Latest Web Content Accessibility Guidelines WCAG 3.0
Implementing the latest WCAG 3.0 guidelines is crucial for accessible web design in 2025. You’ll need to familiarise yourself with new standards, update existing content, and apply proper colour contrast ratios. Ensure text alternatives for non-text content, keyboard accessibility, and correct heading structures.
These steps align with the European Accessibility Act and promote digital inclusion across web and mobile app design.
Familiarise Yourself With WCAG 3.0 Standards
To ensure your website meets the latest accessibility standards, familiarise yourself with WCAG 3.0. This updated guideline, building on the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 and the Web Accessibility Directive, introduces new criteria for HTML structure and interface design. Understanding these standards will help you create more inclusive websites, potentially improving access to health insurance information and other vital services.
Key areas to focus on include:
- Enhanced colour contrast requirements
- Expanded guidance on text alternatives
- Updated standards for keyboard navigation
- New criteria for cognitive accessibility
- Improved guidelines for mobile accessibility
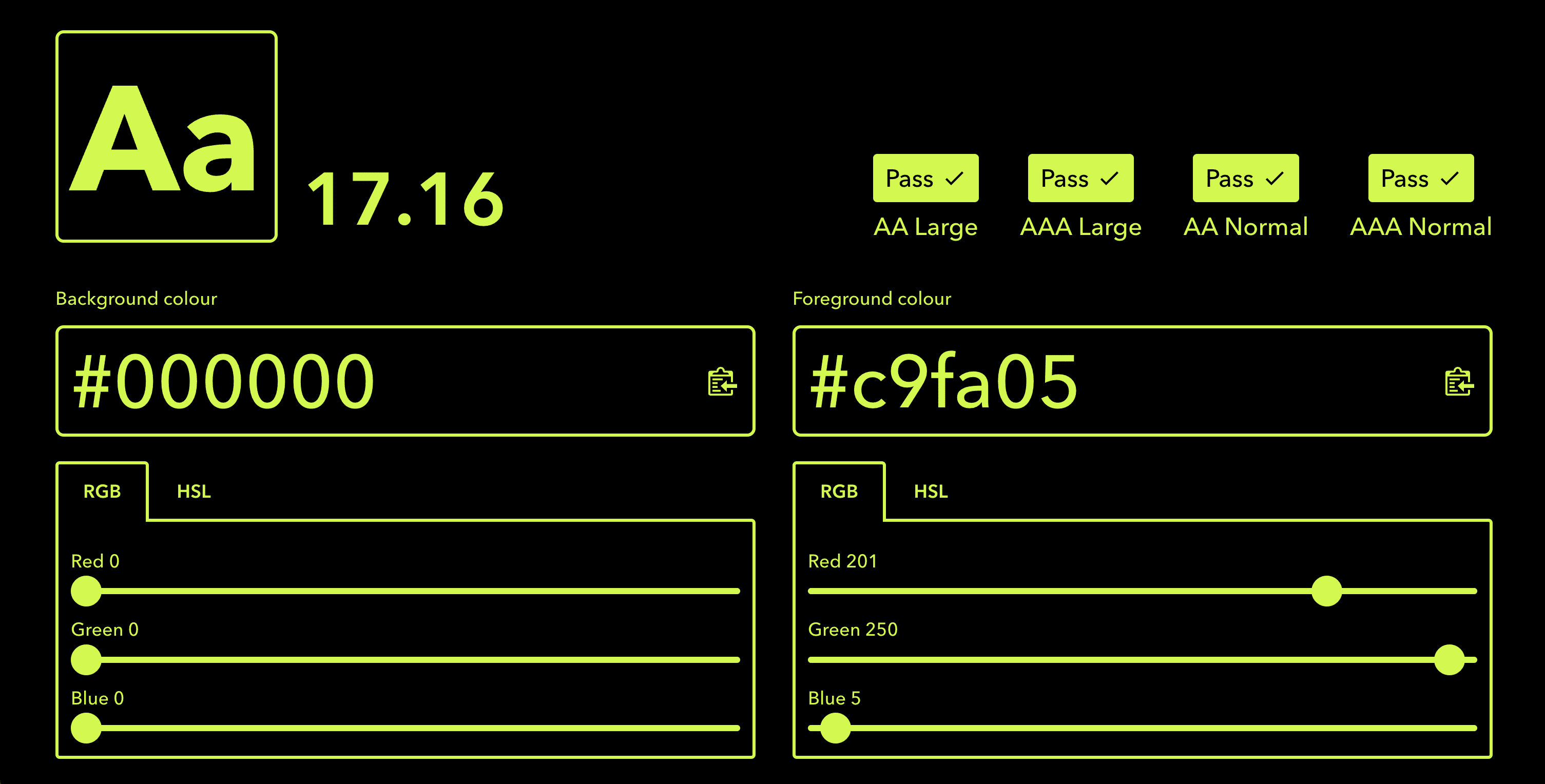
Enhanced colour contrast requirements as shown by https://colourcontrast.cc/
Update Existing Content to Meet New Guidelines
To update your existing content for WCAG 3.0, start by auditing your website using tools like JAWS or a Shopify accessibility app. Improve usability for all user agents, including screen readers and mobile devices. Enhance your content’s structure, ensuring proper headings and semantic HTML.
This will not only boost accessibility but also improve your site’s overall user experience and SEO performance.
Apply Accessible Color Contrast Ratios
To ensure your website meets WCAG 3.0 standards, apply accessible colour contrast ratios. Aim for a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 for normal text and 3:1 for large text. This applies to text overlaid on images as well as interface elements. By implementing proper contrast, you’ll improve readability for users with visual impairments or those accessing your site via broadband on mobile devices.
Remember, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act requires federal agencies and programmes to provide accessible digital content, making this step crucial for compliance.
Provide Text Alternatives for Non-Text Content
To provide text alternatives for non-text content, conduct a thorough audit of your website’s images, videos, and interactive elements. Use descriptive alt text for images, ensuring it conveys the same information as the visual content. Consider providing longer descriptions using the longdesc attribute or linking to a separate page with detailed explanations for complex graphics or charts.
This approach not only aids users of nonvisual desktop access tools but also improves the experience for those using public transport or accessing your site via mobile devices. Remember to regularly update your API documentation to reflect these changes, making it easier for developers to maintain accessibility standards.
Ensure Keyboard Accessibility for Navigation
To comply with WCAG 3.0 guidelines, you must ensure keyboard accessibility for navigation. Make all interactive elements, including video controls and transport options, accessible via keyboard input. Focus on providing clear visual indicators for keyboard focus, maintaining a logical tab order, and ensuring that all functions can be performed without a mouse.
This approach benefits users with motor impairments and those who prefer keyboard navigation, improving overall accessibility and user experience.
Implement Proper Heading and Structure Semantics
To implement proper heading and structure semantics, you must use HTML tags correctly to create a logical hierarchy. This not only aids web accessibility for users with visual impairments who rely on screen magnification but also helps bridge the digital divide.
 Proper structure improves navigation for all users, including those accessing health information online. As web accessibility legislation evolves, maintaining a clear document outline becomes crucial for compliance and ensures both humans and assistive technologies easily understand your content.
Proper structure improves navigation for all users, including those accessing health information online. As web accessibility legislation evolves, maintaining a clear document outline becomes crucial for compliance and ensures both humans and assistive technologies easily understand your content.
Improve Accessibility With AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning offer powerful tools to enhance web accessibility, aligning with the disability rights movement’s goals. You can use AI for automated testing, personalise experiences, and implement voice assistants for improved navigation.
Image recognition aids in creating text alternatives, while chatbots assist users with disabilities. By monitoring user behaviour, you’ll refine accessibility features, ensuring your site’s markup language meets diverse needs.
Use Machine Learning to Personalise User Experience
To enhance accessibility, use machine learning to personalise user experiences on your website. By analysing user behaviour and preferences, you can automatically adjust interface elements, content presentation, and navigation to suit individual needs. This approach aligns with the ADA Amendments Act of 2008, which broadened the definition of disability and helps prevent discrimination by ensuring equal access to digital infrastructure. Implement voiceover features that adapt to user patterns, meeting European Commission guidelines for web accessibility whilst providing a more inclusive online environment.
Apply AI-Powered Voice Assistants for Navigation
Enhance your website’s navigation with AI-powered voice assistants. By integrating advanced speech recognition and natural language processing, you can create a more intuitive interface for users with visual impairments or motor difficulties. Use eye tracking data and cursor movement analysis to refine the voice assistant’s responses, ensuring it provides accurate guidance through your site’s CSS structure and content. This tool not only improves accessibility but also offers a seamless browsing experience for all users.
Employ Image Recognition for Text Alternatives
To enhance web accessibility, employ image recognition technology to generate accurate text alternatives. This approach aligns with the Equality Act 2010, ensuring all users have access to digital content equally. By implementing AI-driven image analysis, you can automatically create descriptive alt text, improving the experience for those using screen readers or other assistive technologies.
Consider using adaptive fonts that adjust based on user preferences, further enhancing readability and motivation for engagement with your content. This technology not only aids in regulatory compliance but also supports inclusive education by making visual information accessible to all:
| Image Type | AI Recognition Feature | Accessibility Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Photographs | Object and scene detection | Detailed descriptions for visually impaired users |
| Infographics | Text extraction and data analysis | Comprehensive summaries of complex information |
| Charts and graphs | Data point recognition | Numerical insights for non-visual access |
| Icons and symbols | Icon classification | Consistent labelling for improved navigation |
Integrate Chatbots to Assist Users With Disabilities
Integrate chatbots into your website to assist users with disabilities, enhancing their experience and access to information. These AI-powered tools can help with tasks like navigating complex documents, understanding graphic design elements, and even placing telephone calls.
Chatbots like Intercom can significantly improve cognition for users struggling with traditional web interfaces by offering real-time support. Ensure your chatbot is designed with accessibility and can adapt its communication style to suit various user needs, including those who might have difficulty processing advertising content or complex visual elements.
Monitor User Behavior to Enhance Accessibility Features
To enhance accessibility features, monitor user behaviour on your website using artificial intelligence tools. Analyse how users interact with your PDF documents, computer hardware interfaces, and brand elements.
This data can help you identify areas where the voluntary sector might struggle, allowing you to make targeted improvements. By leveraging AI to track user patterns, you can create a more inclusive digital experience that adapts to individual needs and preferences.
Prioritise Mobile Accessibility for Inclusive User Experience
To create an inclusive user experience, prioritise mobile accessibility in your web design. Develop responsive layouts for various screen sizes and optimise touch targets for mobile users. Ensure content is accessible without zooming and simplify navigation on mobile interfaces. Provide clear feedback for user interactions and test accessibility across devices. These strategies benefit everyone, from public sector workers to library volunteers using speech recognition.
Design Responsive Layouts for Various Screen Sizes
To ensure your website is accessible across devices, design responsive layouts that adapt to various screen sizes. This approach aligns with the Federal Communications Commission’s guidelines for digital accessibility and supports the Civil Rights Act of 1964 principles by providing equal access to information. Use flexible grids and images, adjusting content ratios to maintain readability on small and large displays. Conduct thorough evaluations of your responsive design to ensure it performs well on different devices, enhancing your site’s search engine optimisation whilst meeting accessibility standards.
Optimise Touch Targets for Mobile Users
To optimise touch targets for mobile users, you need to consider those with intellectual disabilities or using assistive devices like switches. Make buttons and interactive elements large enough for easy tapping, ideally at least 44×44 pixels. This improves confidence in navigation and reduces errors in telecommunications apps. Ensure sufficient spacing between targets to prevent accidental taps, aiding users who struggle with precise movements.
Your layout should facilitate easy parsing of information, enhancing usability for all:
| Element | Recommended Size | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Buttons | 44x44px minimum | Easier to tap accurately |
| Links | Padded to 44x44px | Prevents misclicks |
| Form fields | 48px height | Improves input accuracy |
| Spacing | 8px minimum | Reduces accidental interactions |
Ensure Content Accessibility Without Zooming
To ensure content accessibility without zooming, design your website with readability in mind for both smartphone and desktop computer users. Use responsive typography that scales appropriately across devices, ensuring text remains legible without pinch-zooming. This approach benefits society, reducing the expense of specialised equipment like screen magnifiers. Consider the layout of your content as if it were an elevator pitch – concise, clear, and easily digestible at first glance:
- Set font sizes to at least 16px for body text
- Use relative units (em, rem) for scalable typography
- Maintain sufficient line spacing for improved readability
- Ensure buttons and interactive elements are large enough to tap easily
- Implement a responsive layout that adapts to different screen orientations

Simplify Navigation on Mobile Interfaces
To simplify navigation on mobile interfaces, create a clear and concise menu structure that prioritises equal opportunity for all users. Develop a checklist based on international organisation for standardisation guidelines to ensure your mobile navigation meets accessibility standards.
Consider implementing keyboard shortcuts for quick access to key sections. This will reduce the risk of seizures from excessive scrolling or tapping. Streamlining your mobile navigation will enhance usability for everyone, including those with cognitive or motor impairments.
Provide Clear Feedback for User Interactions
To provide clear feedback for user interactions, consider users with deafness and those relying on speech synthesis. Implement visual cues, haptic feedback, and audio alerts to ensure EN 301 549 standards compliance. Use closed captioning for video content and provide text alternatives for all audio feedback. This approach not only supports accessibility but also aligns with inclusive policy, making your mobile interface more user-friendly for all.
Test Mobile Accessibility Across Devices
To ensure your website’s accessibility across various devices, conduct thorough testing on both iOS and Android platforms. Use tools that simulate different screen sizes and resolutions to check if your design adapts seamlessly. Pay attention to colour contrast and readability, especially for users with colour blindness. This approach improves user experience and boosts your search engine optimisation efforts.
Here’s a testing checklist to guide your mobile accessibility assessment:
| Device Type | Test Focus | Accessibility Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Touch target size | Easier navigation for motor-impaired users |
| Tablets | Content scaling | Improved readability for visually impaired users |
| Older devices | Performance | Ensures access for users with older technology |
| Screen readers | Content structure | Enhanced navigation for blind users |
Optimise Websites for Compatibility With Assistive Technologies
To optimise your website for assistive technologies, focus on implementing ARIA roles, ensuring screen reader compatibility, and supporting voice recognition software. Provide captions and transcripts for multimedia content, enable keyboard-only navigation, and use accessible forms. These strategies enhance learning and feedback for users with disabilities, preventing undue hardship and fostering understanding. By creating a permalink structure that supports accessibility, you’ll improve the overall user experience.
Implement ARIA Roles and Attributes Appropriately
To implement ARIA roles and attributes appropriately, you must focus on enhancing the description of your web elements for universal design. By using ARIA specifications, you’ll improve accessibility for users relying on assistive technologies, such as commuting by bus. This approach supports equal employment opportunity by ensuring all users can access and understand your content, regardless of their abilities.
Ensure Screen Reader Compatibility
To ensure screen reader compatibility, you must structure your content logically and use proper HTML semantics. Examples of semantic elements that clearly defines its content:
<form>
<table>
<article>
Examples of non semantic elements that tell you nothing about its content:
<div>
<span>
This approach combats ableism and helps users in poverty access information effectively. Avoid relying solely on visual cues or animation to convey meaning, which can hinder readability for those using assistive technologies. Instead, focus on creating a precise content sequence that screen readers can interpret accurately, improving the overall accessibility of your website.
Support Voice Recognition Software
To support voice recognition software on your website, ensure all interactive elements are clearly labelled and can be activated through voice commands. This approach benefits consumers using assistive technologies and aligns with the Equality Act’s requirements for digital accessibility. When implementing CAPTCHAs, provide audio alternatives that work seamlessly with voice recognition tools. Consider using test automation to verify voice command functionality across your site, including areas like credit card forms, to ensure a smooth user experience.
Provide Captions and Transcripts for Multimedia
To enhance accessibility, provide captions and transcripts for all multimedia content on your website. This approach ensures that users with hearing impairments or those accessing your site via mobile devices can fully comprehend your content. By offering text alternatives, you’ll comply with regulations and improve your site’s SEO. Remember to use HTTPS to secure the transmission of these transcripts, protecting user privacy and boosting your site’s credibility.
Enable Keyboard-Only Navigation Across Site
To enable keyboard-only navigation across your site, ensure all interactive elements are accessible without a mouse. This approach benefits users with motor impairments and those who prefer keyboard navigation, including lawyers accessing web applications in court. Focus on creating a logical tab order, visible focus indicators, and skip links to the main content. By optimising your site for keyboard navigation, you’ll improve accessibility without significantly increasing development costs. Remember to test your site thoroughly, checking that every pixel is reachable via keyboard, to create a genuinely inclusive user experience.
Use Accessible Forms and Input Fields
When designing accessible forms and input fields, prioritise precise semantics and intuitive typing experiences. Use descriptive labels instead of acronyms, and ensure each field has a visible, associated label. Implement error prevention techniques to reduce the risk of mistakes, especially for users relying on screen readers. Consider offering alternative input methods, such as voice recognition, to accommodate diverse user needs. By creating accessible forms, you’ll improve the overall usability of your website, making it easier for all users to interact with your multimedia content and submit information efficiently.

Test and Audit Accessibility Regularly for Compliance
Regular accessibility testing and auditing ensure your website complies with current standards. Conduct manual tests with users, employ automated tools, and perform routine audits to identify issues. Address problems promptly, document your efforts, and stay updated on accessibility laws. This approach improves perception, protects investment, and prevents complaints, ensuring your site—including its logo and zoom features—remains accessible to all.
Conduct Manual Accessibility Testing With Users
To ensure your website meets accessibility standards, conduct manual testing with users with various disabilities. This approach aligns with the social model of disability, focusing on removing barriers to communication. Involve people with diverse needs in your recruitment process for testers, as they can provide valuable insights into real-world usage. By incorporating their feedback, you’ll not only improve accessibility but also enhance your site’s overall usability, potentially reducing future tax burdens related to non-compliance with technical standards. Here’s a checklist for manual accessibility testing:
- Test keyboard navigation throughout the site
- Verify screen reader compatibility for all content
- Check colour contrast and font readability
- Evaluate form usability and error messaging
- Assess multimedia content for captions and transcripts
Use Automated Accessibility Testing Tools
Use automated accessibility testing tools to enhance your web development process and ensure compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation. These tools can quickly scan your site, including tabs and online forms, flagging potential issues that might hinder users with disabilities. While automated tests shouldn’t replace manual checks, they’re invaluable for ongoing monitoring and can save you time in marketing and maintaining an accessible website.
Perform Regular Accessibility Audits and Reviews
To ensure your website remains accessible, perform regular audits and reviews. Focus on key areas such as government compliance, URL structure, and sound implementation in your information and communications technology. Check luminance levels to maintain proper contrast ratios. By conducting these audits, you’ll identify and address accessibility issues promptly, keeping your site inclusive for all users:
| Audit Focus | Key Elements | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Government Compliance | WCAG guidelines, legal requirements | Avoid penalties, ensure equal access |
| URL structure | Descriptive, logical URLs | Improve navigation for screen readers |
| Sound implementation | Audio alternatives, volume control | Enhance experience for hearing-impaired users |
| Luminance checks | Contrast ratios, colour choices | Ensure readability for visually impaired users |
Stay Updated With Accessibility Laws and Regulations
To stay updated with accessibility laws and regulations, regularly review your WordPress site’s table of contents against current guidelines. Expand your knowledge of digital rights and accessibility standards, including those for augmentative and alternative communication devices. Keeping abreast of changes will ensure your website remains compliant and inclusive, serving all users effectively.
Web Accessibility FAQs
Discover key strategies for accessible web design in 2025. Learn how universal design principles and WCAG 3.0 updates enhance accessibility. Explore AI’s role in improving user experience and the importance of mobile-friendly design. Find out how often to test your site for compliance, ensuring it remains accessible in the context of rapid technological change and economic growth.
How can universal design principles enhance web accessibility?
Universal design principles can significantly enhance web accessibility by creating a more inclusive digital environment for all users. By focusing on flexible, intuitive interfaces that cater to diverse needs, you can make your website ADA-compliant and appeal to a broader market. Consider implementing features that benefit users with various abilities, such as adjustable text sizes and colour schemes, which can aid those with visual impairments or eye conditions. To effectively apply universal design principles, follow these key steps:
- Design for diverse user needs from the outset
- Ensure all content is perceivable through multiple senses
- Create simple, intuitive navigation structures
- Provide ample time for users to interact with content
- Minimise the potential for errors in user interactions
What are the key updates in WCAG 3.0 for web accessibility?
WCAG 3.0 introduces significant updates to improve web accessibility, focusing on a more flexible approach to compliance. You’ll need to adapt your ADA-compliant website test procedures to include new criteria for cognitive accessibility and personalisation. The updated guidelines emphasise the importance of viewport-responsive design, ensuring your content remains accessible across various devices. Shopify ADA-compliant themes must incorporate these changes, particularly in colour contrast and text spacing. Here’s a summary of key updates:
| WCAG 3.0 Update | Impact on ADA Compliant Web Design |
|---|---|
| New scoring system | More nuanced evaluation of accessibility features |
| Enhanced mobile accessibility | Greater focus on responsive design across viewports |
| Cognitive accessibility guidelines | Improved usability for users with cognitive impairments |
| Personalisation options | Increased adaptability to individual user needs |
How can AI and machine learning improve website accessibility?
AI and machine learning can significantly improve website accessibility by automating complex tasks like real-time captioning and image descriptions. These technologies can enhance occupational safety and health by making digital content accessible to all users, aligning with United Nations guidelines.
You can implement AI-powered solutions to optimise scrolling behaviour in Safari, ensuring smooth navigation for users with motor impairments. Moreover, machine learning algorithms can analyse user interactions to adapt interfaces dynamically, meeting the Office for Civil Rights standards.
Why is mobile accessibility crucial for inclusive user experience?
Mobile accessibility is crucial for inclusive user experience as it ensures your website’s menu and content are usable by everyone, regardless of their device or physical limitations. By adhering to international standards for mobile accessibility, you make your site navigable for those who rely on smartphones as their primary means of accessing the internet, including users with disabilities who might struggle with traditional input methods. This approach improves access to essential services like insurance information and metaphorically removes the ‘stairs’ that prevent users from fully engaging with your digital content, creating a more equitable online environment for all.
How often should websites be tested for accessibility compliance?
You should test your website for accessibility compliance at least quarterly, with more frequent checks after significant updates or changes to your content or design. This regular testing ensures your site remains accessible as new features are added or modified, particularly for users who rely on screen readers or other assistive technologies. By incorporating accessibility testing into your routine maintenance, you’ll create a more inclusive digital resource that supports mental health and accommodates service animals, enhancing the overall user experience across various platforms, including macOS. Remember, accessibility is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix, so treat it as you would any other critical aspect of your website’s performance and train your team accordingly.
How often should I test my website for accessibility compliance?
Regular accessibility testing is crucial, ideally conducted monthly or quarterly. However, testing after significant website changes or updates is essential. Automated tools can help with frequent checks, but manual testing should be performed periodically for comprehensive evaluation.
Understanding Web Accessibility Compliance Levels: A, AA, and AAA
Web accessibility compliance levels, defined by the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), are crucial for ensuring that digital platforms are usable by everyone, including people with disabilities. Let’s explore the three levels. A, AA, and AAA, and what do they mean for your website?
Level A: The Basics of Accessibility
Level A represents the minimum requirements for web accessibility. Websites at this level address the most critical barriers that could prevent users with disabilities from accessing content. Compliance at Level A ensures:
- Basic usability, such as providing text alternatives for non-text content.
- Functionality that is navigable without a mouse, enabling keyboard-only users to interact with the site.
- Avoidance of content that might cause seizures, such as flashing images.
This level is foundational and typically integrated during the initial design phase. However, meeting Level A alone may be insufficient for public-facing or high-traffic platforms.
Level AA: The Industry Standard
Level AA is the most commonly targeted compliance level and builds on Level A by addressing broader accessibility issues. It focuses on making content more inclusive and usable for various disabilities. Key features of Level AA include:
- Enhanced contrast between text and background to assist users with visual impairments.
- Clearly labelled navigation to improve usability for screen readers.
- Resizable text up to 200% without breaking the layout or functionality.
Many industries, including healthcare, education, and e-commerce, are required by law or regulation to meet level AA compliance.
Level AAA: The Gold Standard
Level AAA is the highest and most rigorous level of web accessibility. It aims to make content as accessible as possible but may not always be practical for every website. Features at this level include:
- Providing sign language interpretation for all pre-recorded audio content.
- Ensure no reliance on sensory characteristics like colour to convey information.
- Offering detailed navigation and content structure for optimal user experience.
While achieving level AAA is ideal, it is optional and challenging for dynamic or complex websites.
Which Level Should You Aim For?
The level you should target depends on your audience, legal requirements, and the purpose of your platform.
- Level A is a starting point, but more is needed for most public websites.
- Level AA is widely considered the standard for compliance and usability.
- Level AAA is an aspirational goal for those who offer the best possible accessibility experience.
Achieving compliance at any level demonstrates inclusivity and enhances your site’s usability, SEO performance, and user experience.

Final Thoughts
As we approach 2025, implementing accessible web design strategies is crucial for creating inclusive digital experiences that cater to all users, regardless of their abilities. By adopting universal design principles, staying current with WCAG 3.0 guidelines, and leveraging AI and machine learning, you can significantly enhance your website’s accessibility and usability.
Prioritising mobile accessibility and regularly testing for compliance ensures digital content is accessible across various devices and platforms. Ultimately, embracing these strategies not only fulfils legal requirements but also expands your audience reach, improves user satisfaction, and demonstrates your commitment to digital inclusivity in 2025.
As you implement these 2025 strategies for accessible web design, remember that training your team is crucial. Ensure they understand how to create content with various input methods, from trackballs to gesture-based interfaces, to comply with your countries accessibility requirements.
By prioritising accessibility, you’re not just following legal guidelines but opening your digital front door to a broader more inclusive audience. Consider how your site performs across all browsers, including Firefox, Chrome and Bing, to ensure a consistent user experience.
Embrace these strategies as an ongoing commitment to inclusivity. Regular testing and updates will keep your site at the forefront of accessible design, ensuring it remains user-friendly and compliant with evolving standards well into 2025 and beyond.
Ready to open your website to all web users? Let’s discuss how web accessibility impacts your SEO strategy for 2025. Connect with our SEO consultant today and ensure your site is inclusive, optimised, and accessible!



